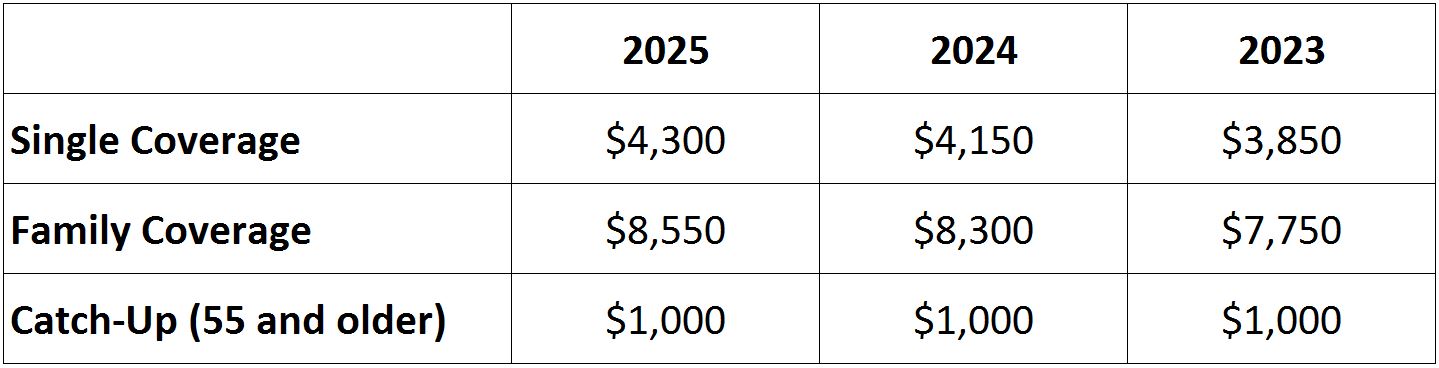An HSA is a tax-favored account used to accumulate tax free/deferred savings. Setting up an HSA account is not required, but encouraged because of the tax benefits. You can fund this account by making a lump sum contribution, monthly contributions or contributions at any interval you choose. HSA plans offer significant premium savings and lower overall financial exposure when compared to most co-pay plans.
These funds can be used to pay for medical expenses that are applied to your deductible & coinsurance or other expenses that may not be covered by your HDHP, such as dental or vision.
What is an HSA?
The concept of a Health Savings Account is to combine a High Deductible Health Plan with a tax-favored Health Savings Account. An HSA is a savings mechanism allowing you to set aside tax-free funds to cover current and future medical, dental or vision needs. HSA plans offer a lower monthly premium compared to co-pay plans.
High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP)
HDHP’s are offered by most major insurance companies and are comprehensive, major medical plans. All covered services are applied to the annual deductible at the contracted price. Premium rates are greatly reduced when the office and prescription co-pays are eliminated. This premium savings can be transferred to your HSA account to be used when needed. Why pay a high monthly premium for a co-pay plan if you are not utilizing this benefit regularly? Or, if you utilize benefits more than the average consumer, why pay a high premium, office co-pays and prescription co-pays when you could meet a deductible and/or coinsurance then should be covered at 100%?
What are the Benefits of an HSA?
HSA accounts provide tax savings when you fund the account and when you use the funds from the account. Your annual contribution reduces your taxable income, and the funds withdrawn for qualified expenses are never taxed. Your Health Savings Account earns interest and grows tax-deferred. At age 65, you can withdraw funds for any non-medical purposes at the ordinary tax rate, or tax free if used for a qualified expense.
Contribution Rules
- Contributions to your HSA account can be made by the account holder, an employer, or a third party on behalf of the account holder.
- Annual individual and family contribution maximums apply and are adjusted each year by the Department of The Treasury.
- Catch-up contributions for individuals and their spouses, over age 55 and not enrolled in Medicare, are available.
- Any unused contributions are automatically rolled over for use in the next calendar year.
Contribution Limits
People with an HSA-qualified High Deductible Health Plan who do not have other coverage that pays prior to the deductible can set aside tax-free dollars to pay for eligible medical expenses. The 2025 HSA contribution limits are summarized in the chart below. There’s a $150 increase for people with single coverage (from $4,150 in 2024 to $4,300 in 2025) and a $250 increase for people with family coverage (from $8,300 in 2024 to $8,550 in 2025). HSA account holders have until April 15 (the tax-filing deadline) to make contributions for the previous year.
Distribution of Funds
- Can be used tax-free for qualified expenses. Note: thanks to the CARES Act, over-the-counter drugs are now an eligible expenses once again.
- Can be used tax-free to pay COBRA or other medical insurance premiums while unemployed or collecting unemployment
- Can be used for qualified dependents who are uninsured
- The funds are always yours. Early withdrawal for non-qualified expenses before age 65 results in a 20% penalty + regular income tax.
At age 65, unused HSA funds can be used for non-qualified expenses with no penalty; ordinary income tax applies.